Currently, one-third of the heat energy supply of the ERZ thermal grid is based on fossil fuels. It has an annual heat demand of 762 GWh. The main heat sources are waste heat from the energy plants at Hagenholz (53%), wood-fired power plants (16%), 12 gas (29%), and oil (2%) boilers. In addition, hot-water buffer storage of 30’000 m3 is also available. The peak demand in winter is roughly 300 MWth, and two-thirds of this is being fulfilled using fossil resources. The current CO2 emissions levels are at 0.1044 kg CO2-eq /kWh. ERZ is looking for concrete measures toward a 100% renewable-based district heating system. To decarbonize the ERZ district heating network, future energy planning should be performed considering Point Carbon Capture Storage/Utilization (CCS/U), diversified energy supply and storage scenarios, temperature reduction, and district heating network expansion strategies. The Urban Energy System Laboratory at Empa, is performing this analysis using the Ehub optimization tool.
Ehub modeling and optimization of ERZ district heating network in Zurich
The Urban Energy System Laboratory at Empa is performing the analysis to decarbonize the district heating network
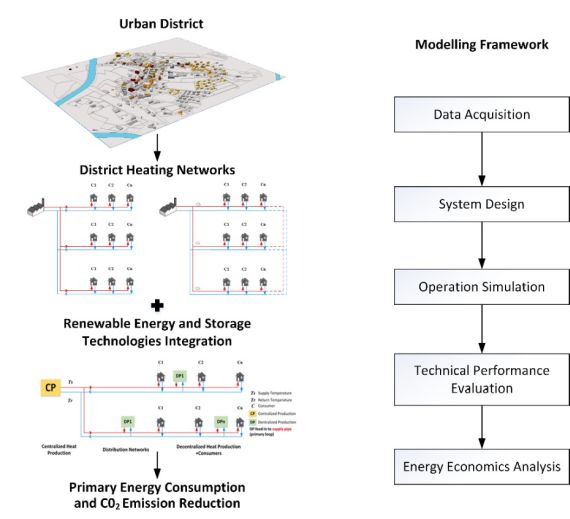
Schematic of modelling framework to assess different thermal networks typologies together with centralized and decentralized renewable feed-in